/home/runner/work/strom/strom/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
Model Cards provide a framework for transparent, responsible reporting.
Use the vetiver `.qmd` Quarto template as a place to start,
with vetiver.model_card()
Writing pin:
Name: 'wd-svm'
Version: 20251124T032611Z-164a4SVM
Before moving forward with the to-do list, let’s throw a Random Forest to it.
SVM
For many reasons, Random Forest is usually a very good baseline model. In this particular case I started with the polynomial OLS as baseline model, just because it was so evident from the correlations that the relationship between temperature and consumption follows a polynomial shape. But let’s go back to a beloved RF.
⏩ stepit 'svm_raw': Starting execution of `strom.modelling.assess_model()` 2025-11-24 03:26:11 /home/runner/work/strom/strom/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning: Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations. ⏩ stepit 'get_single_split_metrics': Starting execution of `strom.modelling.get_single_split_metrics()` 2025-11-24 03:26:11 ✅ stepit 'get_single_split_metrics': Successfully completed and cached [exec time 0.0 seconds, cache time 0.0 seconds, size 1.0 KB] `strom.modelling.get_single_split_metrics()` 2025-11-24 03:26:11 ♻️ stepit 'cross_validate_pipe': is up-to-date. Using cached result for `strom.modelling.cross_validate_pipe()` 2025-11-24 03:26:11 ✅ stepit 'svm_raw': Successfully completed and cached [exec time 0.1 seconds, cache time 0.0 seconds, size 14.8 KB] `strom.modelling.assess_model()` 2025-11-24 03:26:11
Metrics
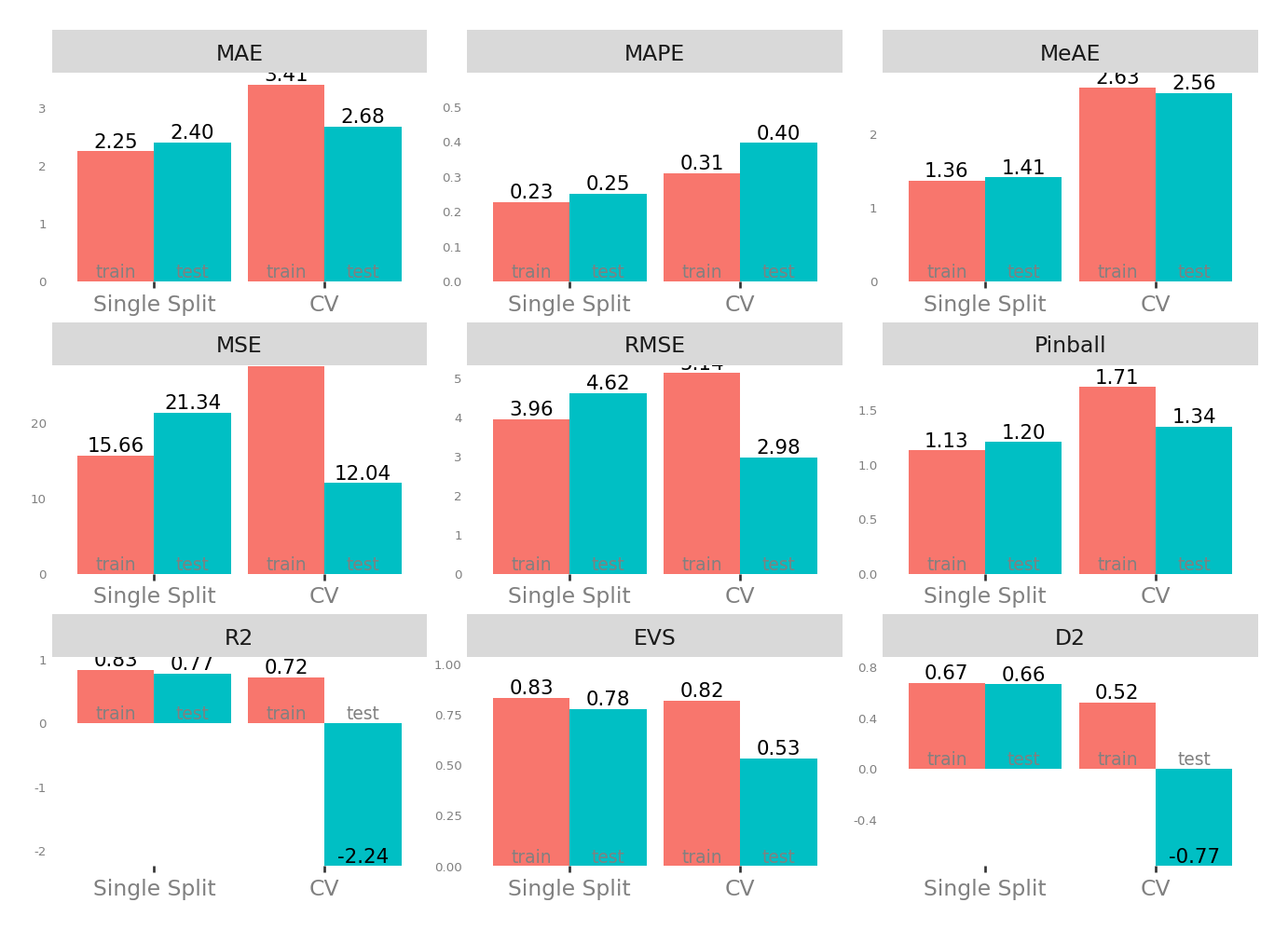
| Single Split | CV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| train | test | test | train | |
| MAE - Mean Absolute Error | 2.253863 | 2.404185 | 2.684980 | 3.410023 |
| MSE - Mean Squared Error | 15.655275 | 21.344099 | 12.038683 | 27.480901 |
| RMSE - Root Mean Squared Error | 3.956675 | 4.619967 | 2.982166 | 5.136139 |
| R2 - Coefficient of Determination | 0.832035 | 0.774003 | -2.236684 | 0.722929 |
| MAPE - Mean Absolute Percentage Error | 0.226225 | 0.250558 | 0.395428 | 0.309699 |
| EVS - Explained Variance Score | 0.833088 | 0.775890 | 0.532616 | 0.818702 |
| MeAE - Median Absolute Error | 1.362887 | 1.408742 | 2.555536 | 2.625422 |
| D2 - D2 Absolute Error Score | 0.674623 | 0.662013 | -0.765698 | 0.520175 |
| Pinball - Mean Pinball Loss | 1.126932 | 1.202092 | 1.342490 | 1.705011 |
Scatter plot matrix
Observed vs. Predicted and Residuals vs. Predicted
Check for …
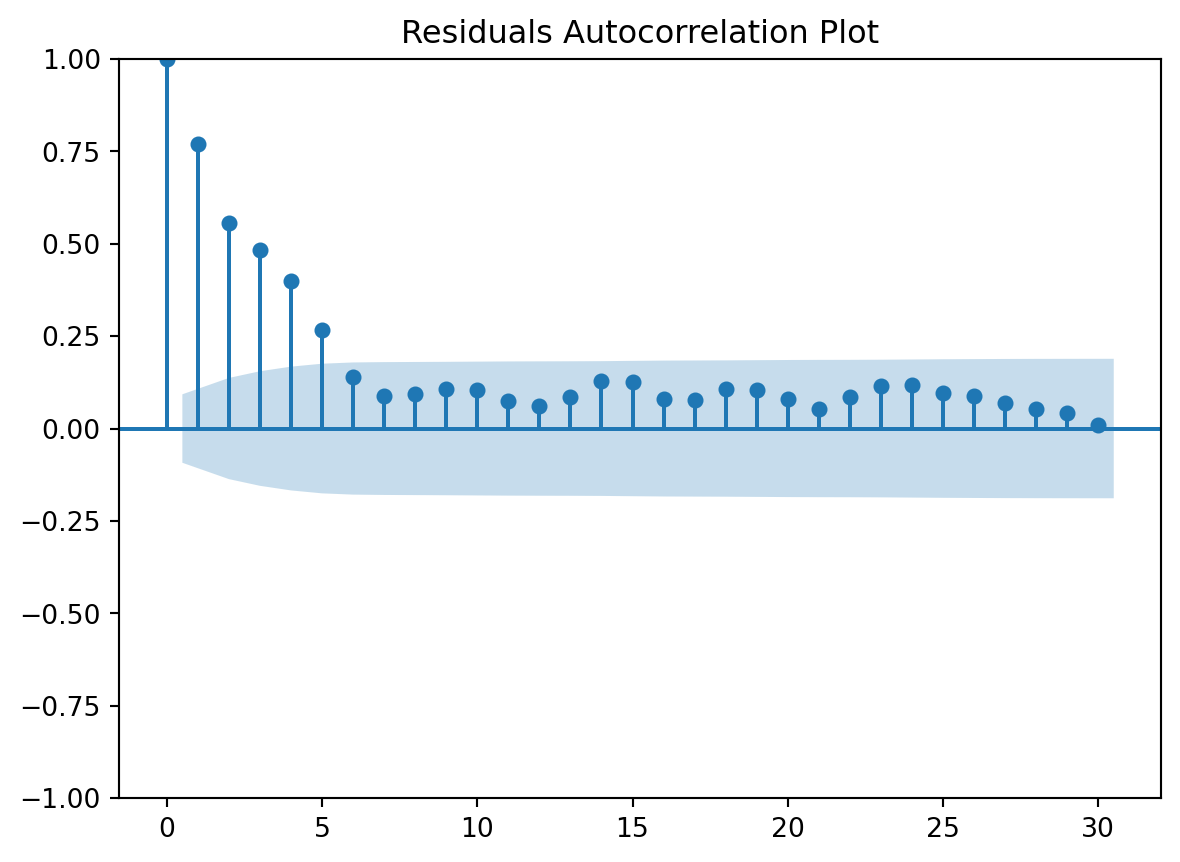
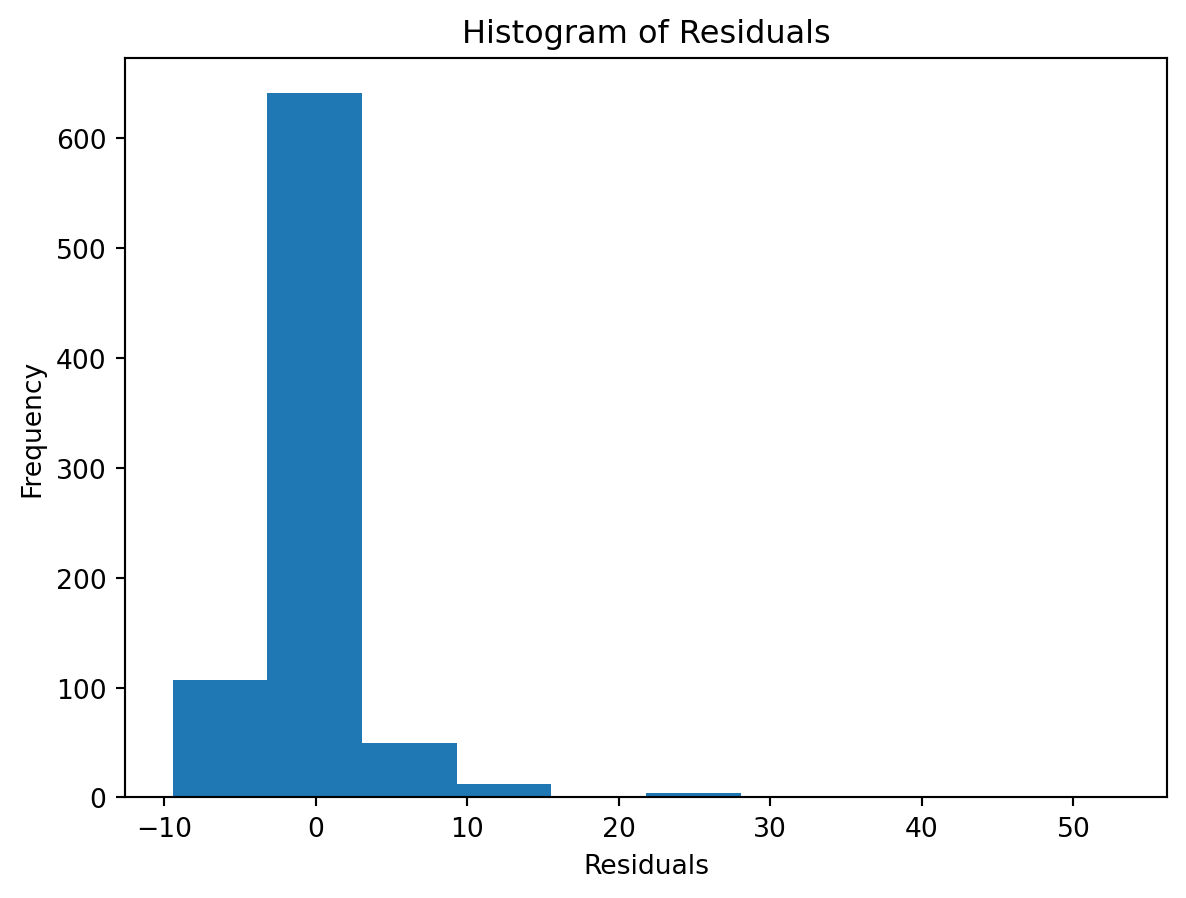
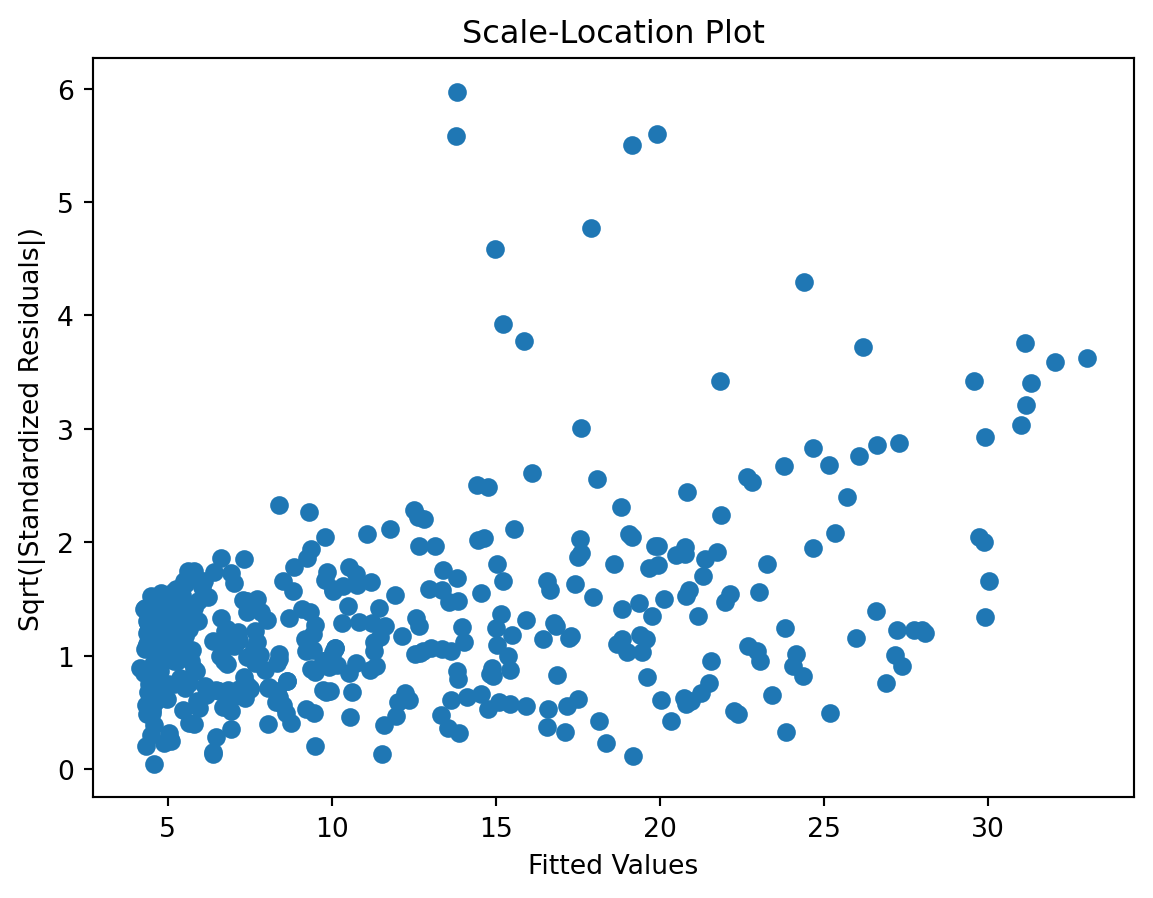
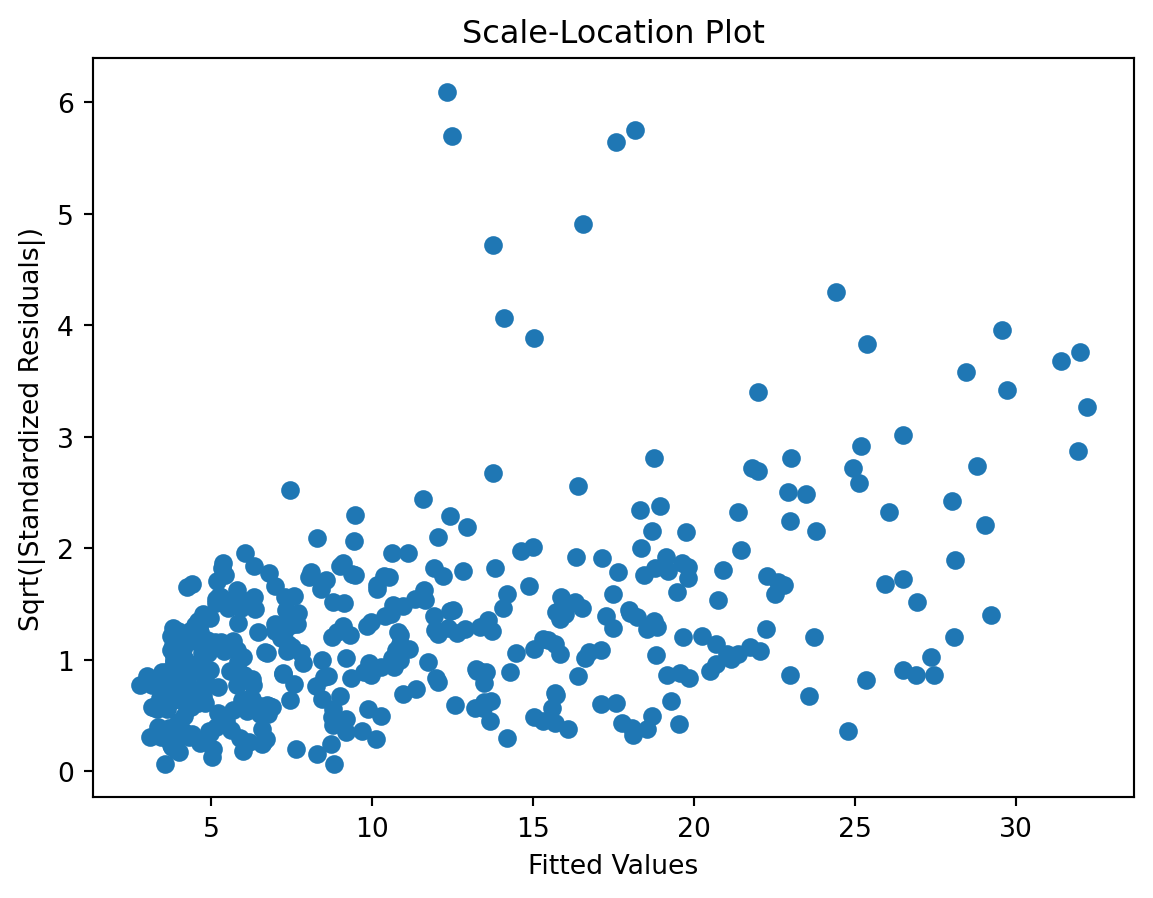
check the residuals to assess the goodness of fit.
- white noise or is there a pattern?
- heteroscedasticity?
- non-linearity?
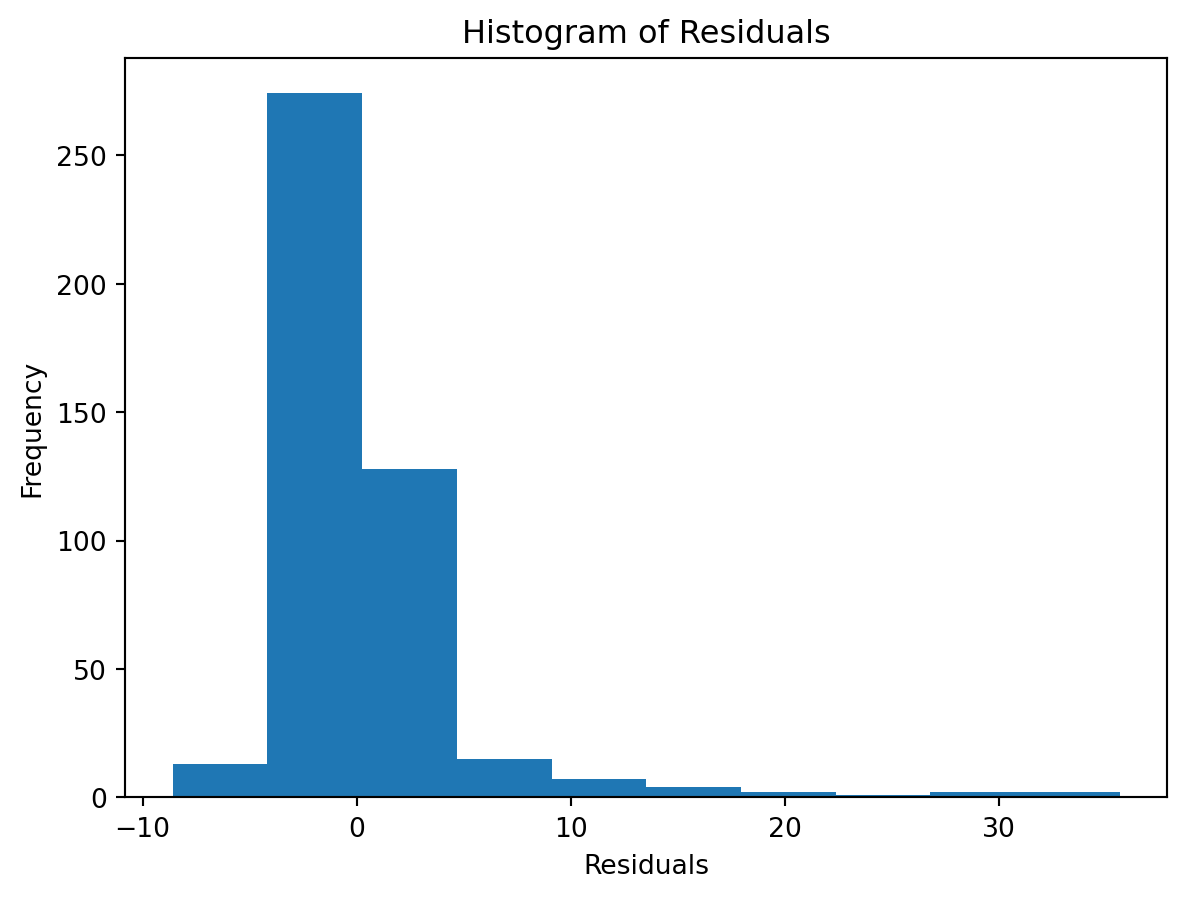
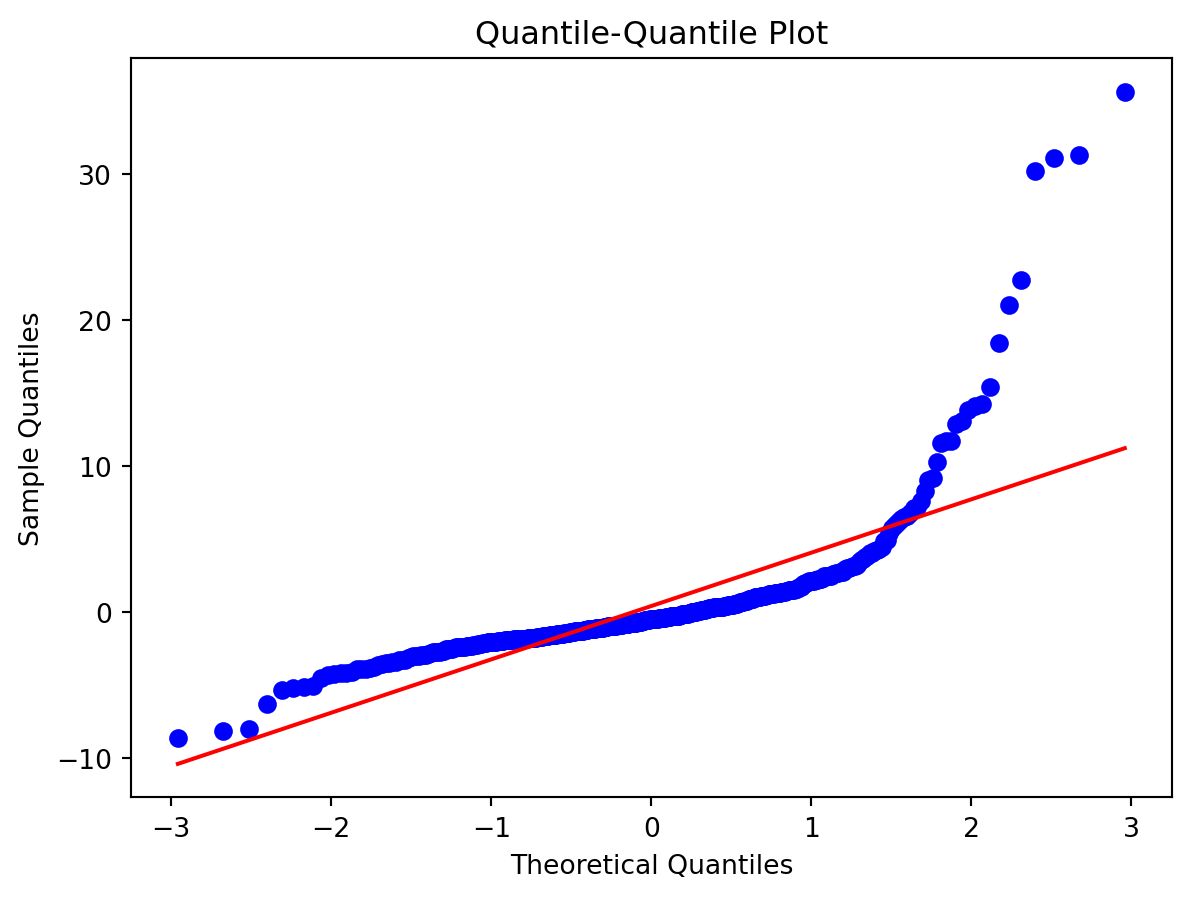
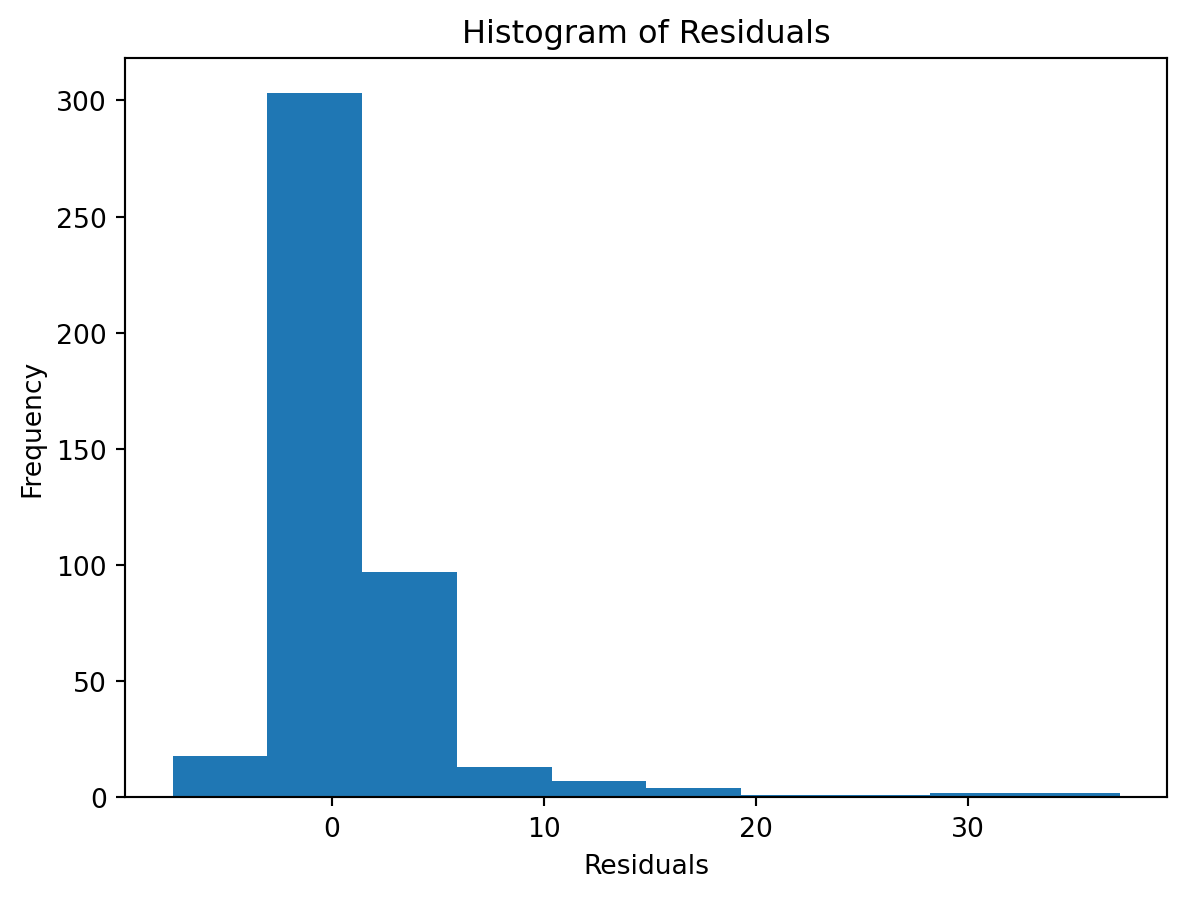
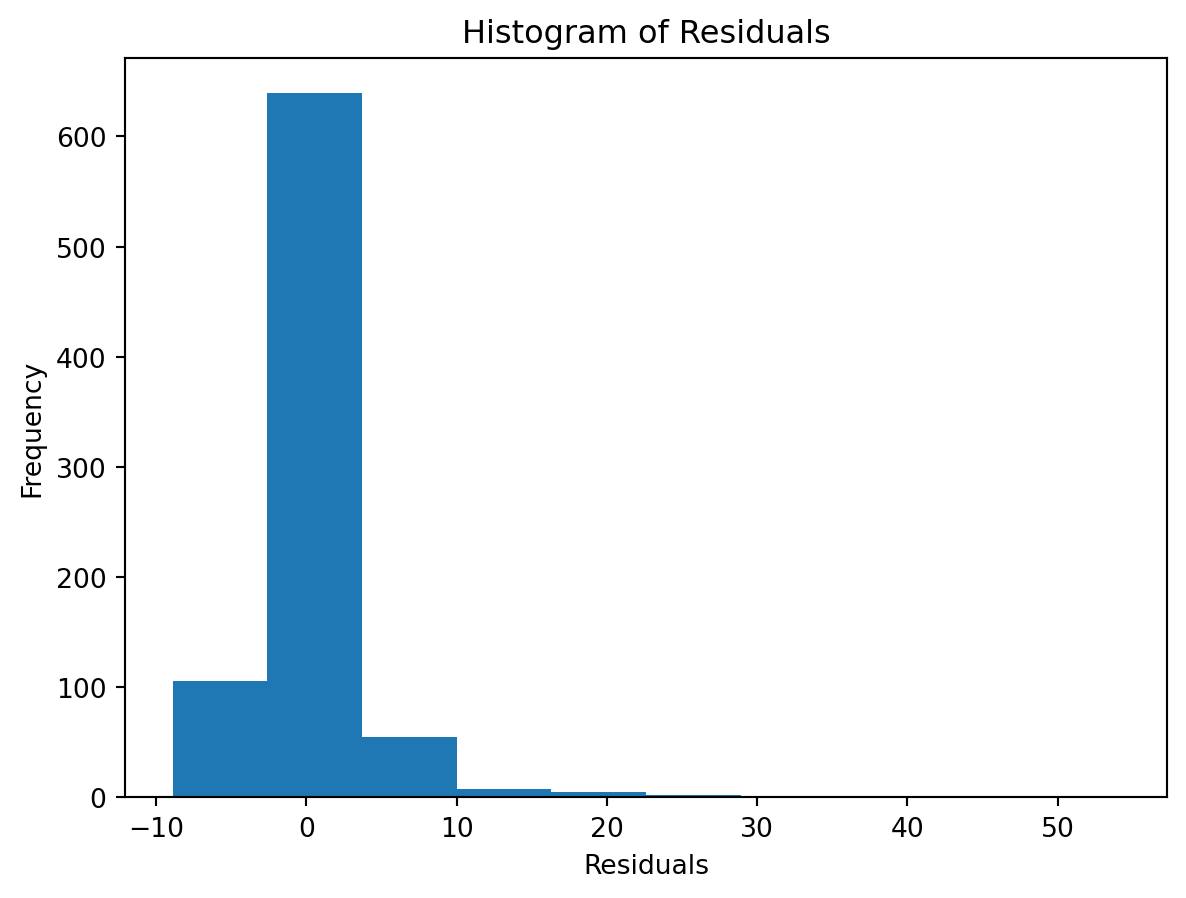
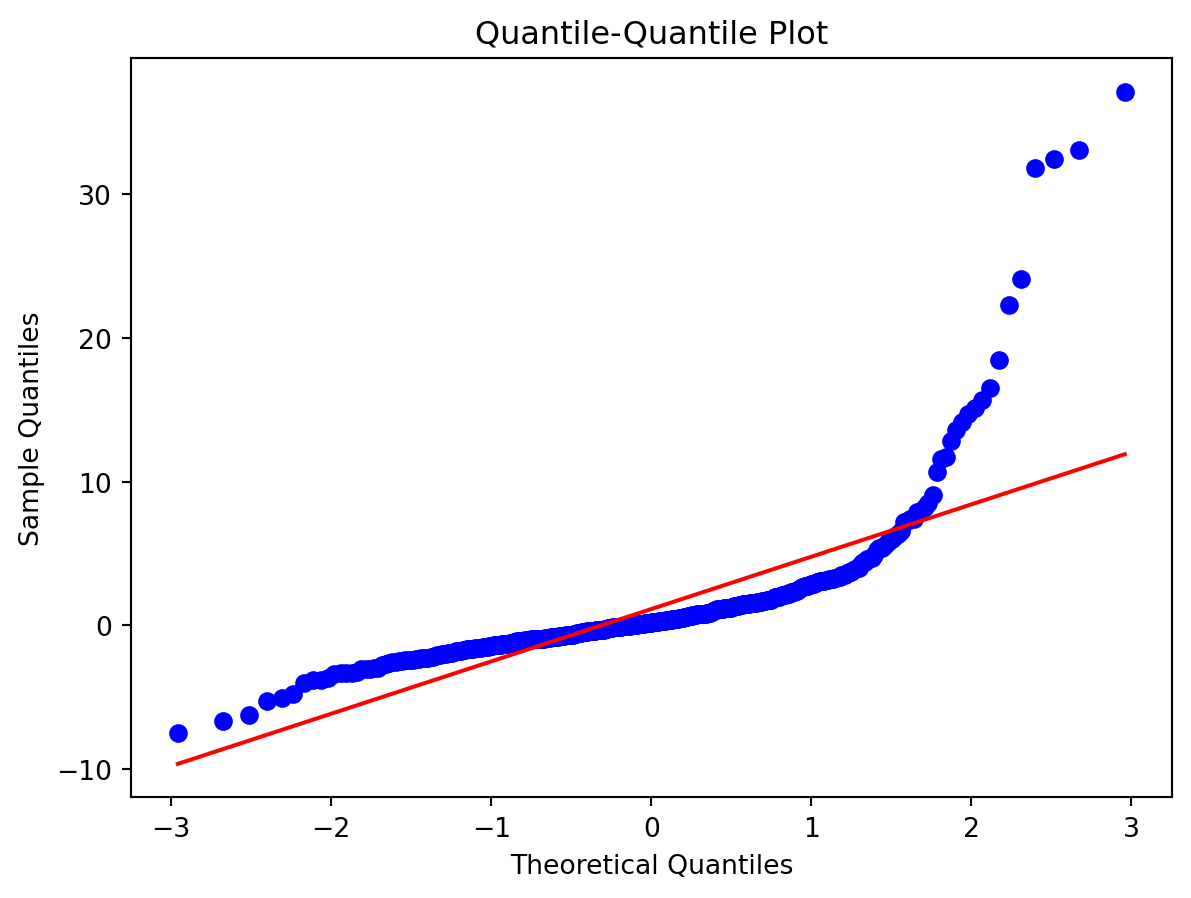
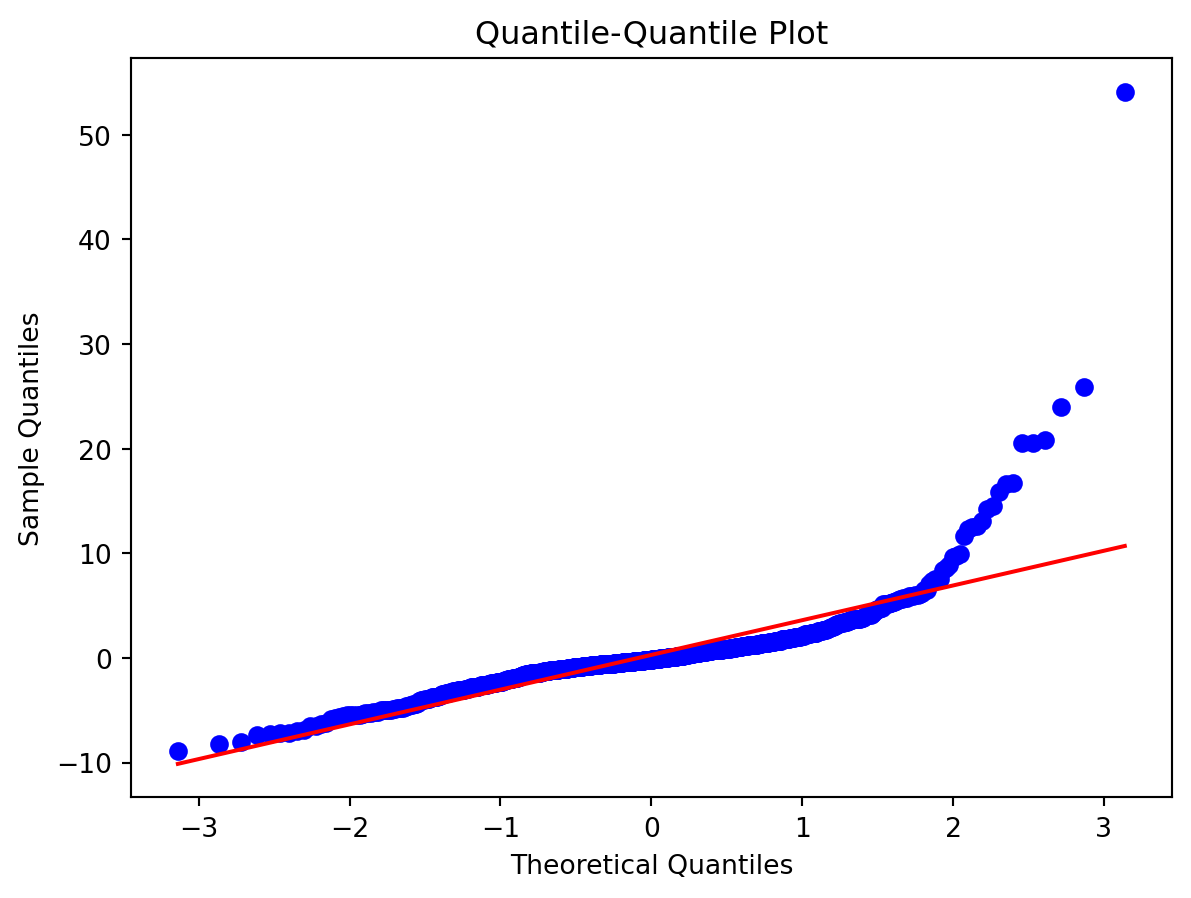
Normality of Residuals:
Check for …
- Are residuals normally distributed?
Leverage
Scale-Location plot
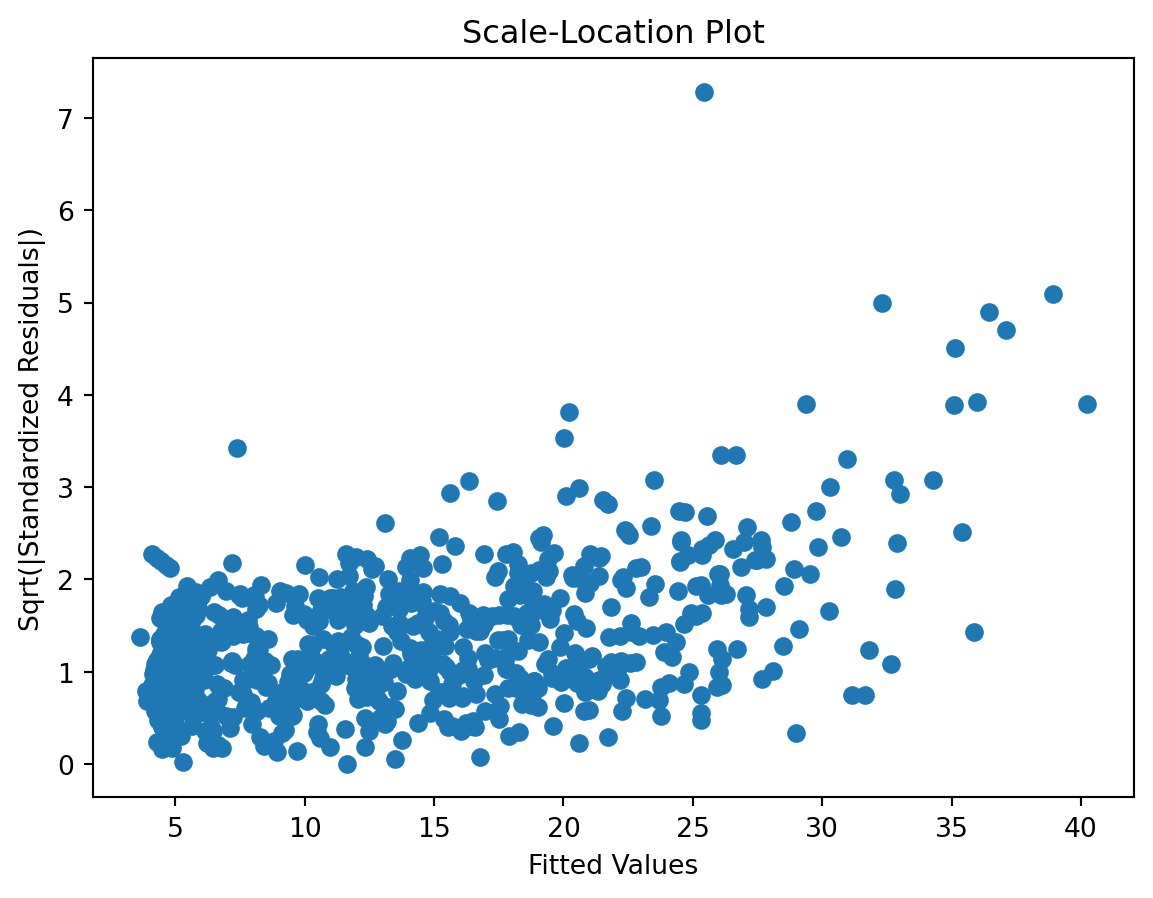
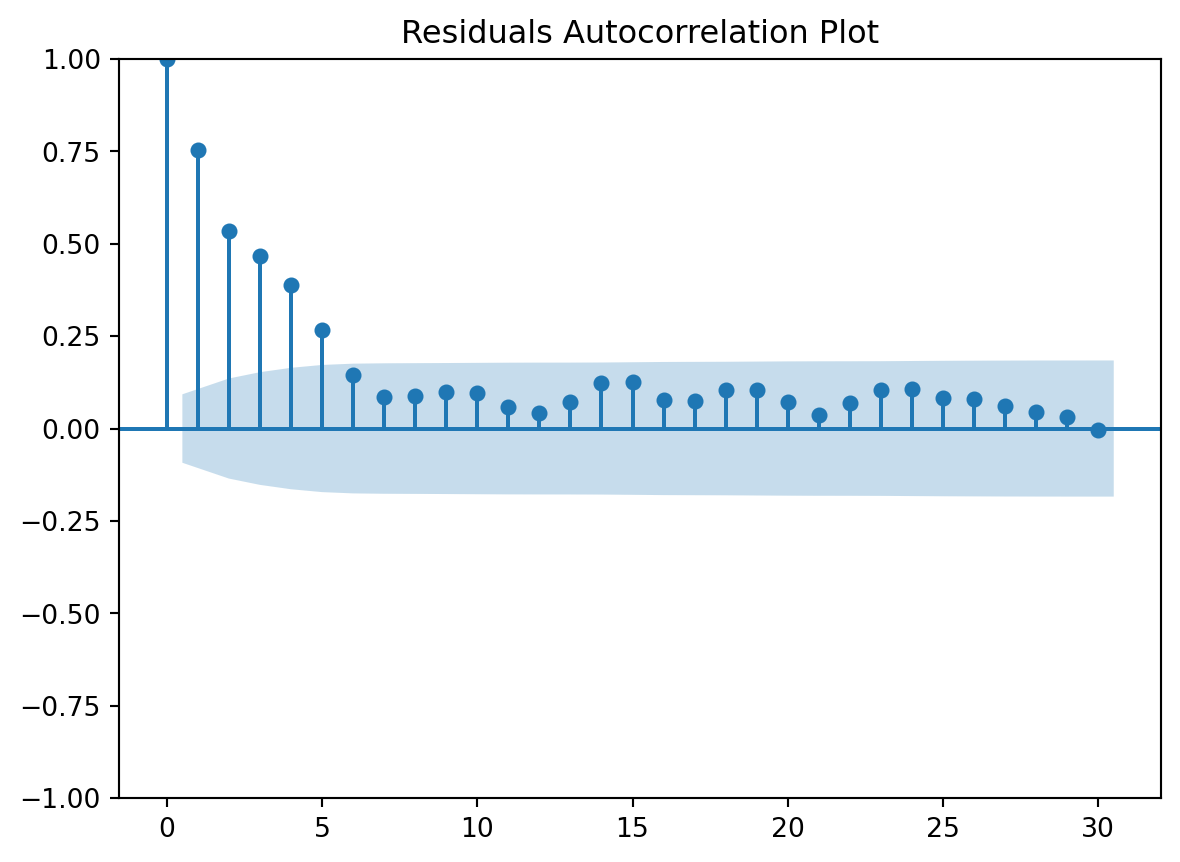
Residuals Autocorrelation Plot
Residuals vs Time
Well, not that bad, but it is overfitting quite a lot.
♻️ stepit 'grid_search_pipe': is up-to-date. Using cached result for `strom.modelling.grid_search_pipe()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15
Model Cards provide a framework for transparent, responsible reporting.
Use the vetiver `.qmd` Quarto template as a place to start,
with vetiver.model_card()
Writing pin:
Name: 'wd-svm'
Version: 20251124T032615Z-37e61
⏩ stepit 'svm_tuned': Starting execution of `strom.modelling.assess_model()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15 /home/runner/work/strom/strom/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning: Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations. ⏩ stepit 'get_single_split_metrics': Starting execution of `strom.modelling.get_single_split_metrics()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15 ✅ stepit 'get_single_split_metrics': Successfully completed and cached [exec time 0.0 seconds, cache time 0.0 seconds, size 1.0 KB] `strom.modelling.get_single_split_metrics()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15 ♻️ stepit 'cross_validate_pipe': is up-to-date. Using cached result for `strom.modelling.cross_validate_pipe()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15 ✅ stepit 'svm_tuned': Successfully completed and cached [exec time 0.1 seconds, cache time 0.0 seconds, size 14.7 KB] `strom.modelling.assess_model()` 2025-11-24 03:26:15
Metrics
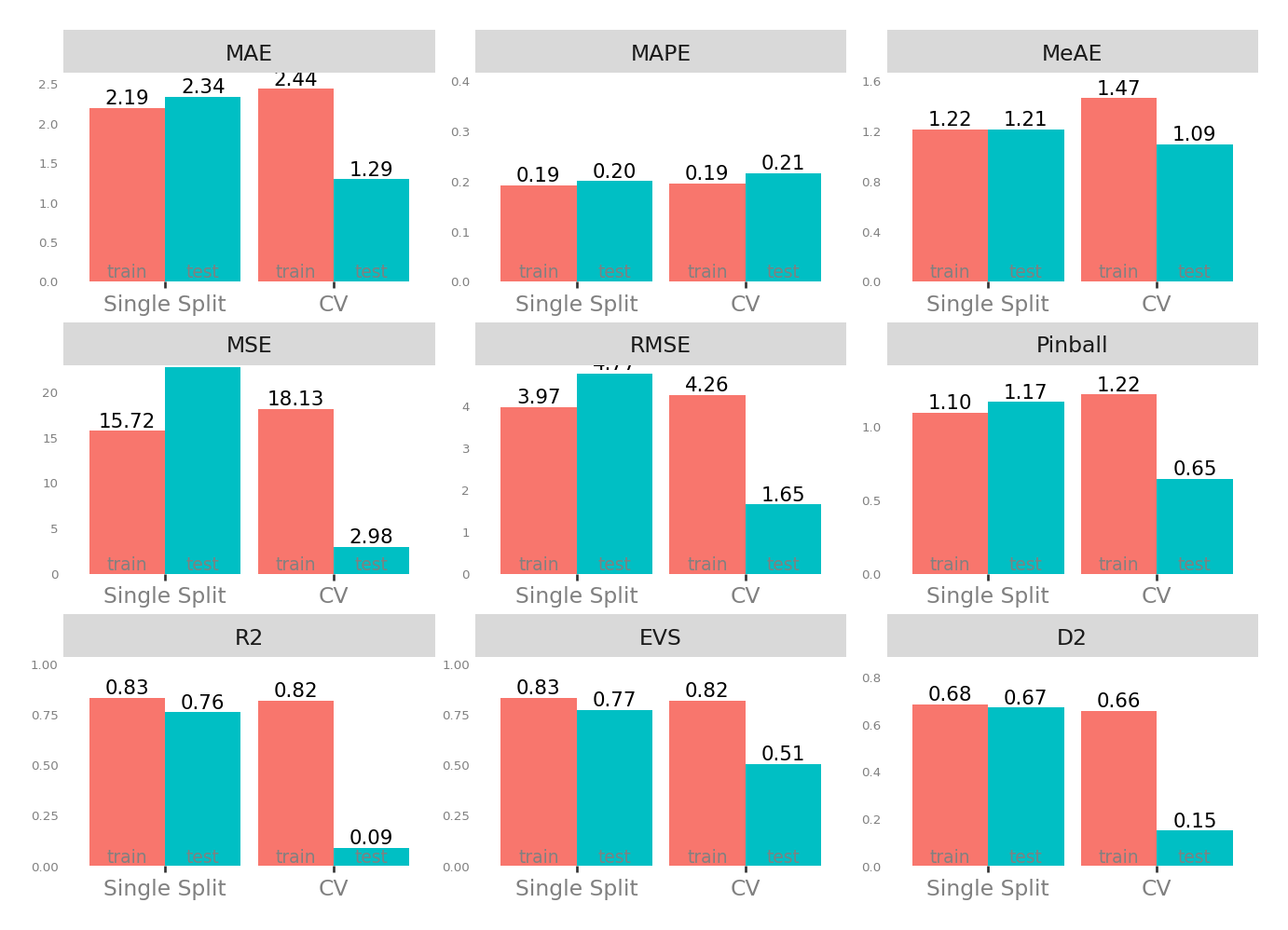
| Single Split | CV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| train | test | test | train | |
| MAE - Mean Absolute Error | 2.191867 | 2.337857 | 1.293039 | 2.436891 |
| MSE - Mean Squared Error | 15.723957 | 22.742093 | 2.980500 | 18.131235 |
| RMSE - Root Mean Squared Error | 3.965344 | 4.768867 | 1.645820 | 4.255542 |
| R2 - Coefficient of Determination | 0.831298 | 0.759200 | 0.090348 | 0.816841 |
| MAPE - Mean Absolute Percentage Error | 0.191461 | 0.199679 | 0.214997 | 0.194748 |
| EVS - Explained Variance Score | 0.832178 | 0.772519 | 0.505620 | 0.817841 |
| MeAE - Median Absolute Error | 1.216609 | 1.212842 | 1.094747 | 1.465526 |
| D2 - D2 Absolute Error Score | 0.683573 | 0.671338 | 0.149081 | 0.656816 |
| Pinball - Mean Pinball Loss | 1.095934 | 1.168928 | 0.646519 | 1.218445 |
Scatter plot matrix
Observed vs. Predicted and Residuals vs. Predicted
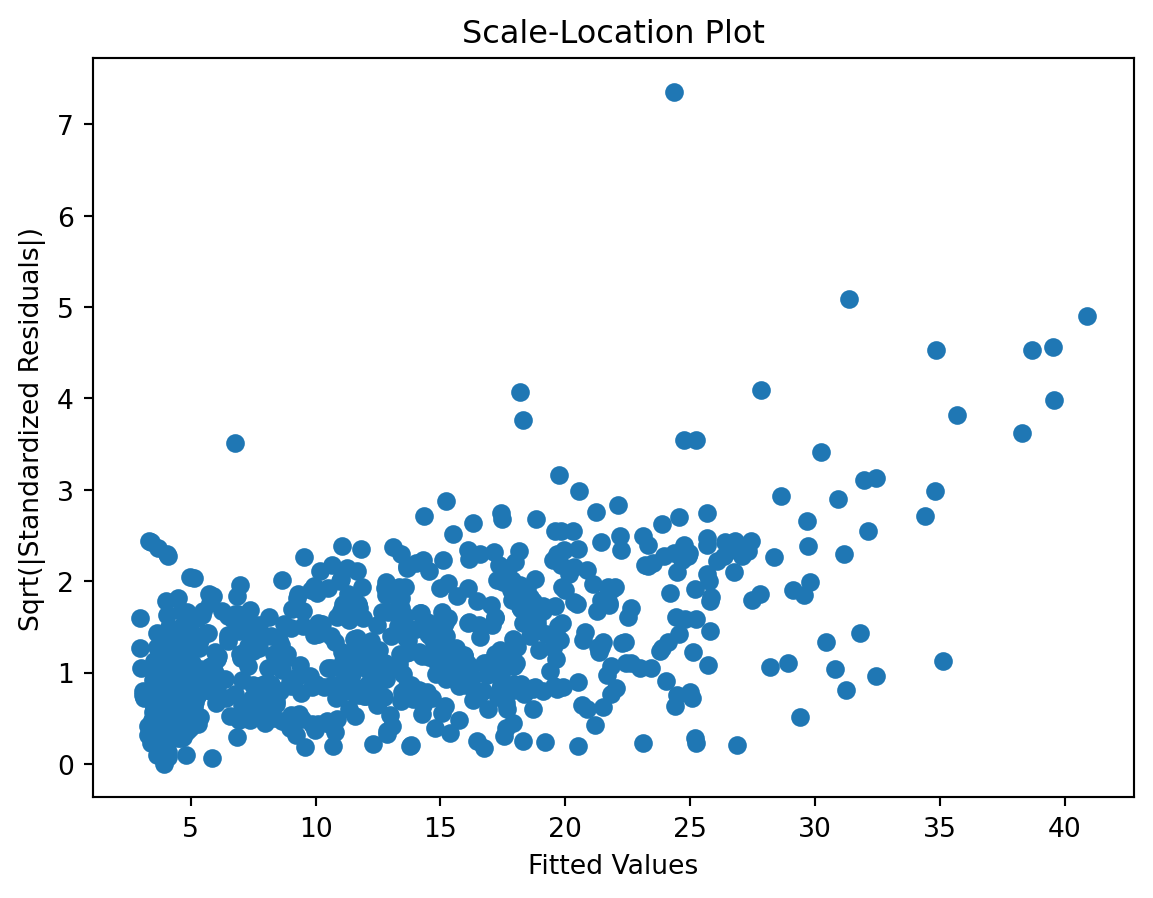
Check for …
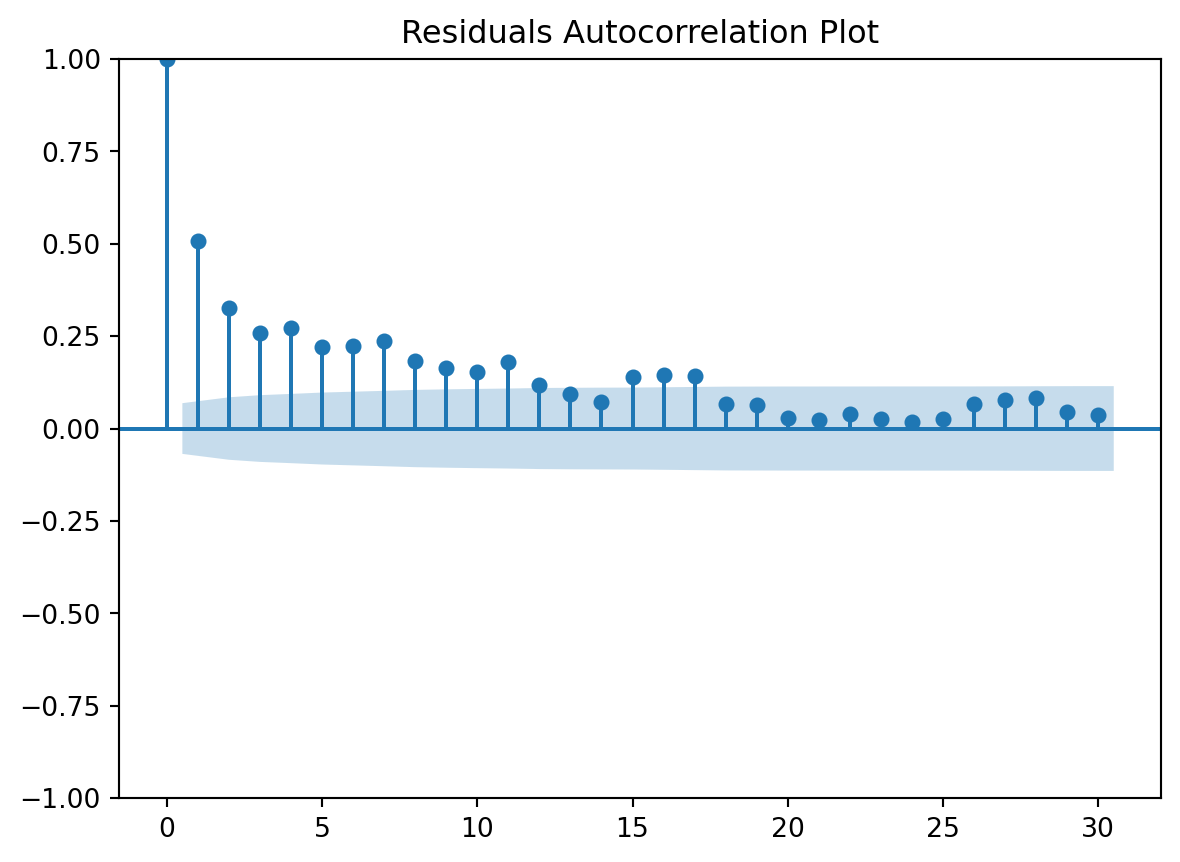
check the residuals to assess the goodness of fit.
- white noise or is there a pattern?
- heteroscedasticity?
- non-linearity?
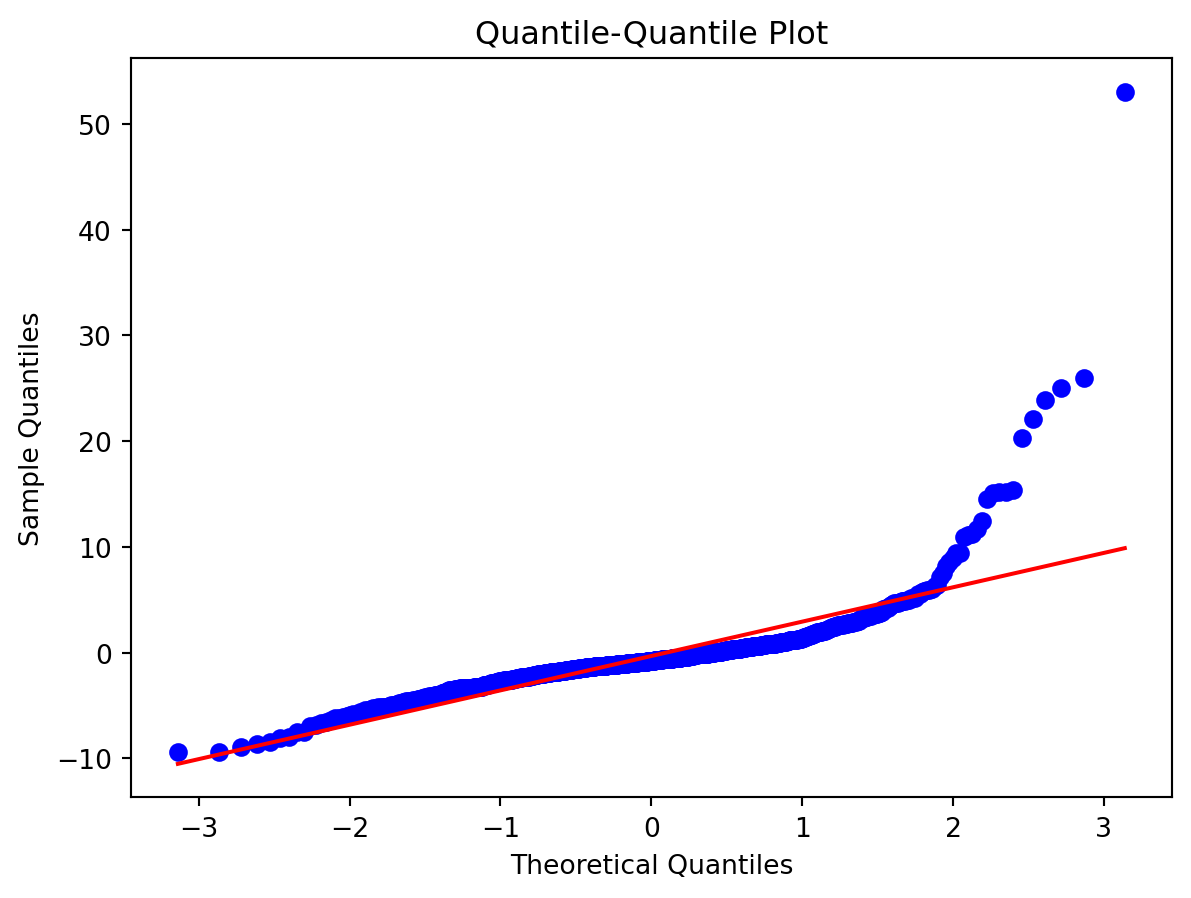
Normality of Residuals:
Check for …
- Are residuals normally distributed?
Leverage
Scale-Location plot
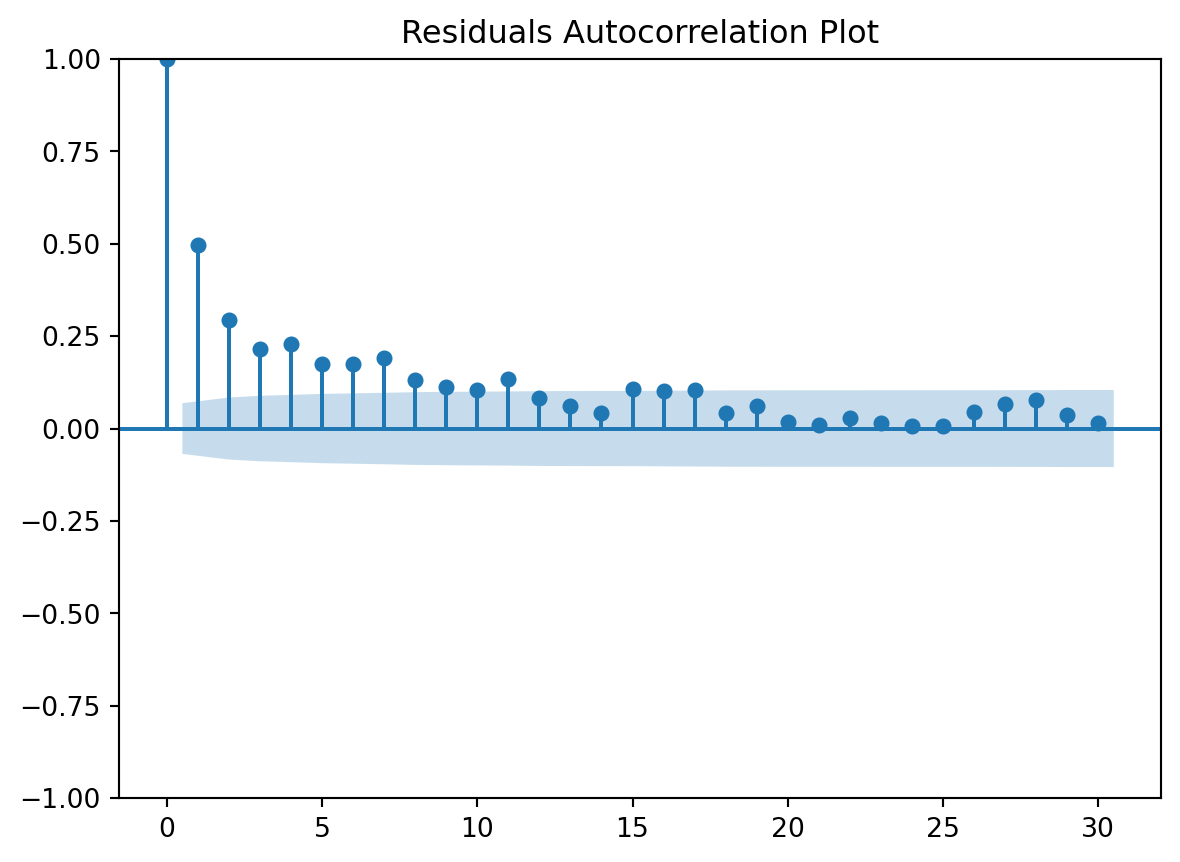
Residuals Autocorrelation Plot